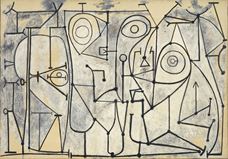
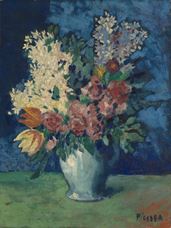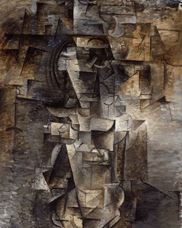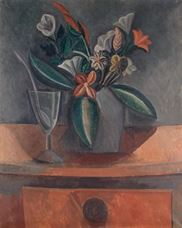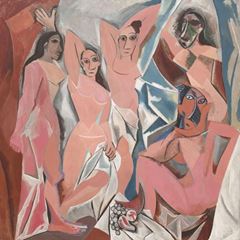Pablo Ruiz Picasso was born on October 25, 1881, in Málaga, Spain. Doña Maria Picasso y López and Don José Ruiz Blasco's first child. Picasso 's father was a painter and painting teacher. He was named while Picasso was baptized "Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de Los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruizy Picasso". Until 1901, he carried the last name of his mother and father. From 1901 he had only used his mother's last name "Picasso".
Picasso spent the first decade of his life in the town of Málaga, where he was born. At the age of ten they moved to La Coruña, north of Spain, where his father will work as art teachers. Picasso attended the art school in La Coruña, where his father was a teacher. His father in a short time realized his son's talent for painting. He was his father who encouraged him to be capable of painting. He took his father as a take an example by in the early days of Picasso painting. He reached the level of his father when he was only 13 years old.
Picasso entered the La Lonja School of Fine Arts in Barcelona in 1895. His father was offered to teach at this school, so his family had moved to Barcelona. He founded his first workshop in Barcelona. Picasso made his first big oil paintings in Barcelona. The "First Holy Communion", dated 1895-96, took part in the most important exhibition in Barcelona. The "Science and Charity" painting in 1897 was praised at the National Fine Arts Exhibition in Madrid and won a gold medal in a competition in Málaga. Picasso moved to Madrid on the same date. He entered the San Fernando Academy, one of the most renowned art schools in Spain. Picasso often visited the Prado Museum rather than the Academy. Soon after, he left because of his illness. He spent several months in Horta de Ebro, a small mountain town in Spain, to fully heal.
In 1899, Picasso returned to Barcelona, which he saw as a city open to modern ideas. He had recovered from his illness and he felt more mature and renovated. In Barcelona, he formed friendships with artists and pioneering intellectuals. His longtime secretary and close friend, poet Jaime Sabartés, met with painter Junyer-Vidal and Carlos Casagemas, with whom he shared the same studio. In Picasso Barcelona, poet Jaime Sabartés met painter Carlos Casagemas and painter Junyer-Vidal. The poet, Jaime Sabartés, would have been Picasso's close friend and secretary in his lifetime. He was going to share the same studio as Carlos Casagemas. Picasso had opened his first solo exhibition in Barcelona in 1900.
In October 1900, Picasso went to Paris for the first time with his friend and artist-friendly Casagemas. Picasso shared his studio in Montmartre with his painter friend Casagemas. He is finished his first painting "La Moulin de la Galette" in Paris. The galleries began to tour; He has seen paintings by artists such as Cézanne, Toulouse-Lautrec, Degas, and Bonnard. He returned to Spain in December. In February 1901, Picasso's painter friend, Casagemas, committed suicide in Paris due to an unhappy love affair. It was a heavy shock for Picasso. His loss of his friend impressed Picasso and his paintings. He began to recognize the darker aspects of city life, and began to depict drunken women, excluded people, people living in poverty and misery. He developed an original style that was completely in contradiction with the currents of the period.
He went to Paris for the second time in May. He opened a workshop on Clichy Boulevard. He opened his first Paris exhibition in the gallery of well-known art dealer Ambroise Vollard. In Picasso's paintings, issues of poverty, deprivation, loneliness and old age gradually were increased. Picasso's paintings were predominantly blue in this period. As a result, this period was named as the "Blue Period" of Picasso. In 1902-1903 he traveled between Paris and Barcelona. In the meantime, during the months he spent in Barcelona, he made the most important paintings of the Blue Period. The Blue Period, which was a direct result of the death of his friend, lasted from the end of 1901 until the end of 1904. For over four years, Picasso never gave up blue, and in his towards the end of the Blue Period, he used green and red in his paintings as indistinct brush strokes.
In 1904 he moved to Paris, where he stayed for a long time. He settled in the Bateau-Lavoir workshop in Montmartre. During this period, Picasso met Fernande Olivier, who would share his life for a long time. Gradually new colors in paintings; light pink, warm red tones, and other light colors began to appear. Picasso began frequent visits to the Médrano Circus, founded on the hillside of Montmartre, with Fernande and his friends. The clowns and circus artists working in this circus near the workshop inspired Picasso's paintings. His themes were taken from the world of the traveling circus. In Picasso's paintings, instead of the beggars and the poor of the Blue Period, these traveler circus people were depicted. This theme was Picasso's main motif at the end of 1904 in the Pink Period. He portrayed clowns and circus workers in his paintings using light shades of pink and orange. Picasso painted these circus workers not only with their glittering situations on the stage, but also their daily life behind the scenes, there sitting in the rest breaks, or their changing states.
In 1907, Picasso visited the Ethnography Museum in Paris, where he examined African sculptures. African art was an important inspiration for Picasso. His painting "The Girls of Avignon", in which he combined geometric abstraction with the effect of African masks, pointed to the path to Picasso's next artistic period. After this artwork, Picasso's works had shifted towards a different Cubist style. Cubism created new radical forms through this painting. "Cubism" became an adventure in which Picasso at that period met together with Georges Braque. The two painters developed analytic cubism in close cooperation, taking the principle of Cézanne's "must be treated with natural, cylinders, spheres and cones". Picasso and Georges Braque used different shades of gray, black, blue, green and soil paint in their paintings. Painters objects; they depicting images they obtained in a complex, opaque and transparent layer, overlapping on each other, visible from several angles. In these pictures, natural forms were reduced to geometric shapes, in particular to cylinders, frames, and cones.
Picasso worked in Horta de Ebro for a few months in 1909. This trip was one of the most productive periods of art life. Picasso made portraits (Woman with Pears) in the Cubist style, with landscapes, pictures of the towns, and Fernande. The Cubist period meant for the rapid recognition of Picasso. He moved to a much larger workshop on Clichy Boulevard near Pigalle Area. In 1911, Picasso's relationship with Fernande had been set in problems and separated.
From 1912 onwards, synthetic cubism emerged. Picasso and Braque, including various objects of ordinary objects and they, created collages and assemblages combining fields made of paint on. With this combination, forms like guitar or bottle, which were similar to familiar objects, had emerged. Picasso had reached the end of his experiments in his 1915 painting "Violin".
In 1916, Picasso met the group of Russian Ballet. In 1917 he went to Italy with this group. He designed decor and costumes for the Russian Ballet group. There he met the Russian ballerina Olga Khoklova, and a year later he married in Paris. In 1921 their son Paul was born. Through the world of ballet, Picasso had established a relationship with the high society, and his marriage to Olga had changed his way of life. During his trip to Italy, Picasso had the chance to visit the places of classical antiquity in the cities of Rome, Naples, and Pompei. In the early 1920s, he created exaggerated figures for unrealistic anatomy. His paintings contained large and disproportionate figures. By taking his figures away format naturalness, Picasso continued his experiments with forms without limit. The way he freely experimented with formats and artistic tools led him to establish a close relationship with surrealists, and he participated in the first surrealist exhibition in 1925. Shortly thereafter, his ties with this group weakened and he decided to go his own way.
From the mid-1920s onwards, Picasso became seriously interested in sculpture. He transferred his experiences in this field to patterns and paintings. There was disagreement in his relationship with his wife Olga. During this period, he met Marie-Thérèse Walter. Marie became Picasso's lover and would be a model for some of his portraits. Picasso painted the Marie-Thérèse while he was sleeping or sitting. In 1930, he settled in the Boisgeloup Castle, near Gisors, north of Paris. He founded a sculpture studio in Boisgeloup. During this period, he made a series of sculptures and busts. In 1935 Marie-Therese and Picasso's daughters known as Maya, Maria de la Concepción were born.
At the beginning of 1937, the Spanish government asked Picasso for a mural for the Spanish section of the World Fair, which will be opened in Paris. The airstrike on “Guernica”, a Basque town in Northern Spain in the Spanish Civil War on April 26, 1937, was the subject of Picasso. Picasso worked unceasingly on “Guernica”, a large-size mural in his new workshop on Grands-Augustins Street. The Yugoslav photographer Dora Maar, whom he met during this period, took many pictures while "Guernica" was being made. Dora would be the model for many of Picasso's paintings.
Picasso had set up a studio at Royan on the Atlantic coast. The painter went and returned between Royan and Paris and continued his work. Picasso was unable to visit his studio in Royan in 1940 with the invasion of Paris. He began to spend his time in the studio at Grands-Augustins Street in Paris. He met Françoise Gilot, a young painter who frequently visited his studio. In the late 1940s, he and Françoise Gilot moved to the La Galloise villa in Vallauris, Southern France. In 1947, Françoise gave birth to their son Claude, and two years later, their daughter, Paloma. Picasso, who continued to experiment with new artistic techniques, was also interested in ceramics to keep him busy for many years. Françoise was frequently involved in the artist's work during this period.
In 1953, after leaving with François, Jacqueline started to live with Roque. Jacqueline was often used as a model in Picasso's paintings. In 1955 they moved to La Californie, a 19th-century manor near Cannes. He made a series of workshops at the La Californie workshop, including Picasso, "The Studı of "La Calıfornıe" at Cannes" and "Jacqueline in Studio". Here, he turned to the works of the old masters and his meeting with the old masters became the main theme of his later works. Picasso also made a diversity of the Spanish palace painter Diego Velázquez's famous painting in 1656, "Las Meninas".
In 1958 he left La Californie workshop and moved to the 14th-century castle of Vauvenargues overlooking the Sainte-Victoire Mountain near Aix-en-Provence, where Cézanne also once lived. He continued his work on painting series. Picasso began to make a diversity of Edouard Manet's famous painting in 1863, "The Luncheon on the Grass". Picasso emphasized the subject of "painter and model" in the variations of his work "The Luncheon on the Grass".
In 1961, Picasso finally moved to the villa of Notre Dame de Vie in Mougins. In the same year, he married Jacqueline Roque. During this period, he continued his variations on the portrait of Jacqueline. At the end of his life, his productivity increased more than ever and he produced numerous works. In this period, Picasso limited himself to the themes of art that had been processed and known in art history. He also used more the traditional motif which depicted the painter and his model.
Pablo Picasso lost his life on April 8, 1973, at the age of 91 in the Notre Dame de Vie residence in Mougins.
Bibliography;
Walther, I.F., (2005). Picasso, Birinci Basım, Taschen/Remzi Kitabevi, İstanbul.
Spence, D., (2012). Büyük Ressamlar Picasso, İkinci Basım, Koleksiyon Yayıncılık, İstanbul.
Buchholz, E.L. ve Zimmermann, B., (2011). Picasso, Literatür Yayıncılık, İstanbul.
Lunday, E., (2013). Büyük Sanatçıların Gizli Hayatları, Beşinci Baskı, Domingo Yayınevi, İstanbul.
Gombrich, E.H., (2002). Sanatın Öyküsü, Üçüncü Baskı, Remzi Kitabevi, İstanbul.
Farthing, S., (2014). Sanatın Tüm Öyküsü, İkinci Baskı, Hayalperest Yayınevi, İstanbul.
Richard, L., (1999). Ekspresyonizm Sanat Ansiklopedisi, Üçüncü Basım, Remzi Kitabevi, İstanbul.
Şenyapılı, Ö., (2003). Ressamlar ve Kadınları, Odtü Geliştirme Vakfı Yayıncılık ve İletişim A.Ş. Yayınları, Ankara.
Bell, J., (2009). Sanatın Yeni Tarihi, Birinci Baskı, NTV Yayınları, İstanbul.
Çev:Öztürk, Ş., (2015). Picasso, İkinci Baskı, Yapı Kredi Yayınları, İstanbul.
1881 He was born in Spain, Málaga on 25 October.
1888-89 He started painting with the lessons he got from his father.
1891 The family moved to La Coruña.
1892 He started art school in La Coruña.
1895 He moved to Barcelona and entered the "La Lonja art" academy where his father was a teacher.
1896 He founded his first workshop in Barcelona. The first large-size oil painting was exhibited in the "First Communion".
1897 He made his second large painting oil painting of "Science and Charity". He studied at the San Fernando Academy in Madrid for a while and left school in the middle of the year.
1898 He went to Horta de Ebro, a small mountain town in Spain.
1899 He returned to Barcelona. He often went to the café called "Els Quatre Gats (Four Cat)". Picasso met poet Sabartés, painter Junyer-Vidai, Nonell, Sunyer, Casagemas, sculptor Hugué. Poet Sabartés would have been Picasso's secretary and close friend throughout his life.
1900 He went to Paris for the first time in October. He shared the studio in Montmartre with Casagemas. Picasso finished his first painting in Paris, "La Moulin de la Galette".
1901 Casagemas shot himself in Paris. Picasso moved to Madrid and went to Paris for the second time in May. He rented a workshop in Clichy Boulevard. He opened his first Paris exhibition at the "Ambroise Vollard Gallery". He began to sign the paintings under the name of his mother's last name"Picasso". Life in Paris was reflected in his work. He used blue and green colors profusely and often. Picasso's Blue Period began.
1902 He's back in Barcelona. Blue monochrome pictures multiplied. He used to develop his blue style. In October, he went to Paris for the third time. He stayed with the poet Max Jacob.
1903 He returned to Barcelona in January. He made more than fifty pictures including tı Life “. He began to use the intense hues of blue.
1904 He settled in Paris. He moved to the "Bateau-Lavoir" workshop in Montmartre. Picasso was going to have a seven-year relationship with Fernande. A seven-year relationship with Fernande. Picasso often visited "Médrano Circus" and "Lapin Agile". He made paintings of clowns and circus artists. Blue Period ended.
1905 He met Apollinaire, Leo, and Gertrude Stein. He often made fairy acrobats and circus paintings. The Pink Period began.
1906 He was influenced by the exhibition of the Iberian statues in the Louvre. Henri Matisse met André Derain and Kahnweiler, who traded art. "Pallet Self-portrait" had the effect of Iberian sculptures.
1907 He saw the African sculptures at the Paris Museum of Ethnology. He made his first cubist work, "The Girls of Avignon" before the "Cubist Era" began. He met Georges Braque.
1909 He developed analytical cubism. Horta entered a productive period in the Ebro. He made portraits of landscapes, towns, and Fernande in an analytic cubist style. He moved to a workshop in Clichy Street near Pigalle Area.
1912 He went on to the Synthetic phase of Cubism. He started making his first paper stickers (papiers colles).
1917 In Rome, the Russian impresario joined Diaghilev's community. He worked on the decor and costumes of the ballet. He met Russian ballerina Olga Khoklova.
1918 The society around him due to ballet caused changes in lifestyle. He married Olga.
1921 His son, Paul (Paolo) was born. He made a few large paintings, which included "The Three Musicians" paintings and monumental figures.
1925 He took part in the first mixed exhibition of surrealist painters. There were problems in her marriage.
1927 He met seventeen-year-old Marie-Thérèse Walter.
1930 He bought the Boisgeloup Castle near Gisors, north of Paris.
1932 He used Marie-Thérèse as a model in a series of paint of blond women sitting or lying.
1935 One of his most important works, "Minotauromachie" he made. Maria de la Concepción (Maya), the child of Picasso and Marie-Thérèse Walter, was born. Jaime Sabartés became Picasso's friend and secretary.
1936 The Spanish Civil War began on July 18th. He met Yugoslav photographer Dora Maar.
1937 Moved to the new workshop at Grands Augustins Street. After the Germans attacked Guernica on April 26, he painted a large wall called Guernica for the Spanish pavilion of the World Exhibition in Paris.
1939 Guernica was exhibited in America. It was in Paris when the Second World War broke out. He departed for Royan, where he stayed intermittently until December.
1940 He shuttled back between Royan and Paris. German troops occupied Belgium and France. Picasso returned to Paris. He moved to his workshop at Grands Augustins Street. He handed over photographs of Guernica to his German officers. "Did you do this?" those who ask, "No, you did!" he responded.
1943 He met Françoise Gilot, a young painter who visited him frequently in the studio.
1947 Françoise and Picasso's first children, Claude was born. He and his family moved to the villa of La Galloise in Vallauris.
1949 The girls of Picasso and Françoise Gilot were born in Paloma. He rented an old perfume factory to use as a ceramic workshop.
1953 Picasso left Françoise Gilot. He met Jacqueline Roque.
1954 He made paintings for the "Painter and Model" series. He made portraits of Jacqueline.
1955 He bought La Californie villa in Cannes.
1956 He made a series of workshops at the La Californie workshop, including Picasso, "The Studı of "La Calıfornıe" at Cannes" and "Jacqueline in Studio".
1957 Picasso has made a variation on the painting "Las Meninas" by Velázquez in La Californie workshop.
1958 He bought the Castle of Vauvenargues near Aix-en-Provence.
1959 He started to make variations on Manet’s picture called "The Luncheon on the Grass".
1961 Picasso and Jacqueline Roque got married. He moved to the Notre Dame de Vie villa near Cannes.
1973 He lost his life on April 8, 1973, at the age of 91 in the Notre Dame de Vie residence in Mougins.